Accidentally sent an email you regret? Learning how to recall an email in Outlook can save you from embarrassing mistakes, confidential information leaks, or sending messages to the wrong recipients. This comprehensive guide walks you through the entire process of recalling emails in Microsoft Outlook, including when the feature works, why it sometimes fails, and alternative solutions when recall isn’t available. Whether you’re using Outlook desktop, web, or mobile, we’ll cover everything you need to know to manage your sent messages effectively.
Quick Answer: How to Recall an Email in Outlook
To recall an email in Outlook, open your Sent folder, double-click the message you want to recall, click “Message” (or “Actions”), select “Recall This Message,” and choose whether to delete the unread message or replace it with a new version. This feature only works if the recipient hasn’t opened the email yet, and it’s most effective when both sender and recipient use Microsoft Exchange servers within the same organization.
What You Will Need
Before attempting to recall an email in Outlook, gather these requirements:
- Microsoft Outlook access: Desktop version (2010 or later) or Outlook on the Web
- Exchange Server: Both sender and recipient must use Exchange-based email (corporate accounts typically qualify)
- Unopened email: The recipient must not have read the message yet
- Time window: Ideally within 1-2 minutes of sending, though effectiveness decreases rapidly
- Same organization: Both parties should be on the same Exchange server for best results
Time estimate: 2-5 minutes | Difficulty level: Beginner | Success rate: 30-70% depending on conditions
Step 1: Locate Your Sent Email in Outlook
Your first action is finding the message you want to recall. This step is essential because you cannot recall an email you cannot access.
Open Microsoft Outlook and navigate to your Sent Items folder. In Outlook Desktop, this appears in the left sidebar under your mailbox folders. Look for the email you need to recall by scanning the sender (should be you), recipient name, and subject line. If you sent multiple emails recently, use the search function by pressing Ctrl+F and typing the recipient’s name or a keyword from the subject line. Act quickly—the sooner you recall a message, the higher your chances of success, as the recipient may open it at any moment.
Once you’ve located the correct email, note the timestamp to confirm you’re selecting the right message. Double-check the recipient address to ensure this is the email you intended to recall.
Step 2: Open the Message Details
Opening the full message details is necessary to access the recall feature. This step gives you complete control over the email’s fate.
Double-click the email in your Sent Items folder to open it in a separate window. The message will display in full, showing the recipient(s), subject line, timestamp, and body content. You’ll notice the ribbon menu at the top of the message window contains the tools you need. Do not forward or reply to this message—doing so may trigger delivery before you can recall it. Take a moment to verify this is definitely the email you want to recall before proceeding to the next step.
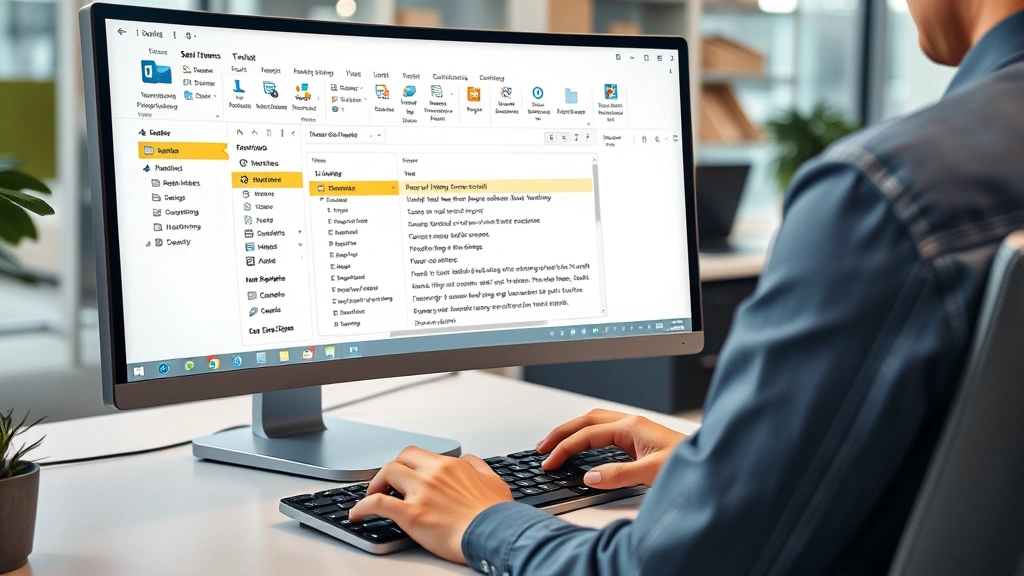
[IMAGE_1: Hero image showing Outlook desktop with Sent Items folder open and a highlighted email message ready for recall]
Step 3: Access the Recall Feature in Outlook
Accessing how to recall an email in Outlook depends on your Outlook version and interface. This step connects you to the actual recall mechanism.
In Outlook Desktop (2016 and later): Look for the “Message” tab in the ribbon menu at the top of the open email. Click “Message” and locate the “Actions” dropdown button. Click “Actions” and you’ll see “Recall This Message” as one of the options. In Outlook 2013 and earlier: The path is “File” → “Info” → “Resend or Recall.” On Outlook on the Web (Outlook.com or Office 365): Open the email from Sent Items, click the three-dot menu (More options), and select “Recall This Message.” If you don’t see the recall option, your email account may not be on an Exchange server, which means recall functionality isn’t available.
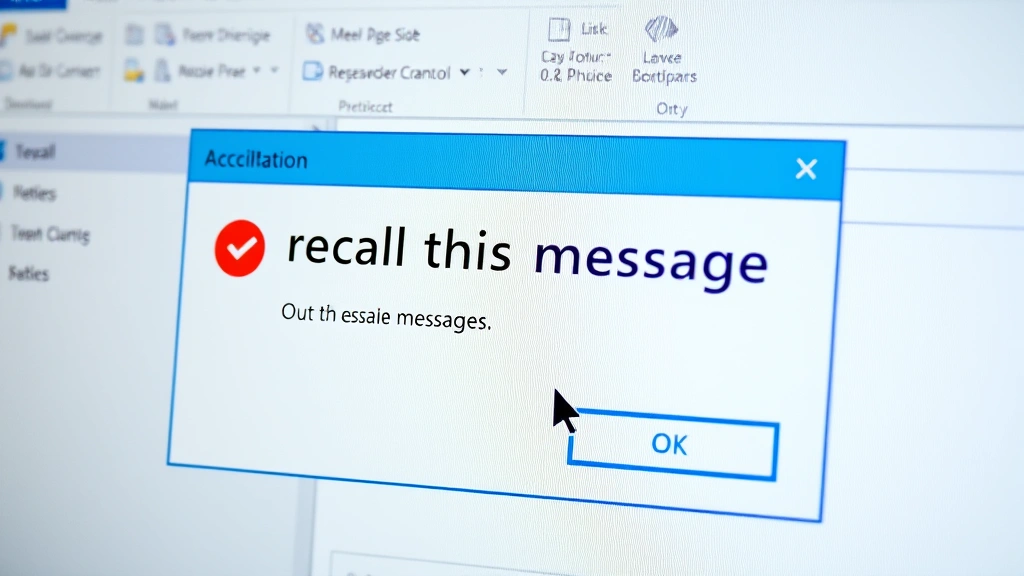
Step 4: Choose Your Recall Action
When you select recall, Outlook presents two options for managing the sent message. Your choice determines what happens to the original email.
A dialog box will appear asking you to choose between two actions:
- Delete unread copies of this message: This option attempts to remove the email from the recipient’s inbox if they haven’t opened it. The original message vanishes without replacement.
- Delete unread copies and replace with a new message: This option removes the original and sends a corrected version. Use this if you need the recipient to receive updated information.
Consider your situation carefully. If the email contains sensitive information you don’t want them to see at all, choose option one. If you made a minor error and want to send a corrected version, choose option two. Note: Even if recall succeeds, the recipient may see a notification that you attempted to recall the message, which could raise questions.
[IMAGE_2: Close-up screenshot of the Recall This Message dialog box with both action options clearly visible]
Step 5: Confirm and Send Recall Request
Finalizing the recall request completes the process. This step sends your recall command to the recipient’s server.
After selecting your preferred action, click “OK” or “Send” to submit the recall request. Outlook will process the command and attempt to recall the message from the recipient’s mailbox. You’ll receive a confirmation message indicating that the recall request has been sent. This does not guarantee success—if the recipient opened the email before the recall request arrived, the original message remains in their inbox. Outlook will send you a notification within a few minutes indicating whether the recall succeeded or failed. Check your Inbox for this status notification to confirm the outcome.
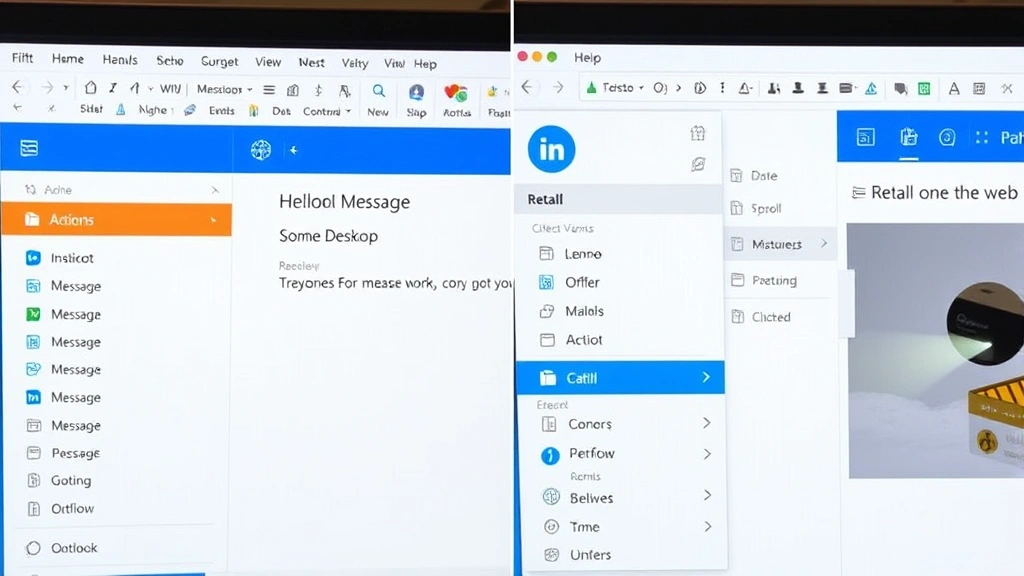
Desktop vs. Web: Key Differences When Using Outlook
Understanding platform differences helps you recall emails effectively regardless of which Outlook version you use. Desktop and web versions have distinct workflows.
Outlook Desktop Application: Offers the most reliable recall functionality. Access the feature through the Message tab and Actions dropdown. Works best with Exchange Server accounts and provides immediate status feedback. Recall works on emails sent within the last 1-2 minutes most effectively.
Outlook on the Web (OWA): Provides recall functionality but with more limitations. The feature appears in the More options menu (three dots) when viewing sent emails. May have longer processing times and reduced success rates compared to desktop. Works only if both parties use the same Exchange organization.
Outlook Mobile Apps: Unfortunately, recall functionality is not available on Outlook for iPhone, iPad, or Android. If you sent an email from mobile, you must use a desktop or web browser to attempt recall.
[IMAGE_3: Side-by-side comparison showing the recall option locations in Outlook Desktop and Outlook on the Web interfaces]
Pro Tips for Email Recall Success
Expert strategies increase your chances of successfully recalling emails in Outlook:
- Act immediately: Attempt recall within 30-60 seconds of sending. Each passing minute reduces success probability significantly.
- Check recipient status: If possible, verify the recipient hasn’t read the email before attempting recall. Look for read receipts or out-of-office messages.
- Use “Replace” strategically: When replacing a message, keep the subject line identical so the system correctly links the recall to the original email.
- Verify Exchange status: Confirm both your account and recipient accounts use Microsoft Exchange. Recall doesn’t work with Gmail, Yahoo, or other non-Exchange providers.
- Follow up with a phone call: For critical errors, don’t rely solely on recall. Call or message the recipient directly to explain the situation.
- Enable read receipts: Request read receipts on important emails going forward. This lets you know immediately if someone opened a message before you can recall it.
- Use delay send: Set up a 2-5 minute delay on outgoing emails. This gives you a window to recall before delivery completes. In Outlook Desktop, use File → Options → Mail → Sending options → Delay Delivery.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Recalling Emails
These errors reduce your recall success rate significantly:
- Waiting too long: Attempting recall more than 5 minutes after sending rarely succeeds. The recipient likely opened the email already.
- Assuming it works: Recall requests often fail silently. Don’t assume success without confirmation. Check the status notification Outlook sends.
- Recalling to external recipients: Email addresses outside your organization (Gmail, Yahoo, Hotmail) cannot receive recall requests. Save this feature for internal corporate emails.
- Changing subject lines: If you replace a message, keep the subject identical. Changing it may cause the recall to fail or create confusion.
- Recalling multiple times: Sending multiple recall requests for the same email looks suspicious and doesn’t improve success rates.
- Ignoring offline status: If the recipient is offline, recall has a better chance of working, but this window closes quickly once they reconnect.
- Not considering read receipts: Forgetting to check if the recipient opened the email wastes time on recall attempts that will certainly fail.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you recall an email in Outlook after the recipient opens it?
No, recall in Outlook only works if the recipient hasn’t opened the email yet. Once they read the message, the recall feature cannot remove it from their inbox. This is why acting quickly—within seconds of sending—is critical for successful email recall.
Does Outlook recall work with Gmail or Yahoo Mail recipients?
Unfortunately, no. How to recall an email in Outlook only functions when both sender and recipient use Microsoft Exchange servers, typically within corporate environments. External email providers like Gmail, Yahoo, and Hotmail don’t support Exchange recall protocols.
What happens when an email recall fails?
When recall fails, the original email remains in the recipient’s inbox, and they may receive a notification that you attempted to recall it. Outlook will send you a status message indicating the recall failed. In this case, consider reaching out to the recipient directly to explain the situation or request they disregard the original message.
Can you recall an email you sent to a distribution list?
Recall becomes significantly less reliable when you’ve sent to distribution lists with many recipients. The feature must process recall requests to each member individually. Success rates drop substantially, and at least one recipient likely opens the email before recall processes. For sensitive information going to groups, avoid email entirely and use a secure announcement method instead.
How long does an email recall take to process?
Outlook processes recall requests almost instantaneously on your end, but the actual recall message must travel to the recipient’s Exchange server. This typically takes 1-3 minutes. However, if the recipient opens their email during this window, recall fails. The sooner you initiate recall after sending, the better your chances of success.
Is there a way to prevent accidental emails in the future?
Yes! Enable the “Delay Delivery” feature in Outlook to automatically delay all outgoing emails by 2-5 minutes. This creates a safety window where you can recall emails before they’re delivered. Go to File → Options → Mail → Sending options and check “Delay Delivery of All Messages.” You can also set this per-email by using the “Delay Send” button when composing messages.
Alternative Solutions When Recall Isn’t Available
If recall fails or isn’t available, these strategies minimize damage:
- Send an immediate follow-up: Send a new email explaining the error and providing corrected information. Make the subject line clear, like “CORRECTION: Previous Email.”
- Contact the recipient directly: Call, text, or message the person immediately. Explain the mistake and ask them to disregard the original email.
- Use email retraction tools: Third-party services like Boomerang offer enhanced email control features, though these work primarily with Gmail.
- Request the recipient delete it: Politely ask the recipient to delete the email without reading it. This works best for time-sensitive mistakes.
- Escalate internally: If the email affects business operations, inform your supervisor or relevant department to manage the situation.
Understanding how to recall an email in Outlook empowers you to manage communication mistakes effectively. While the feature isn’t foolproof, knowing when and how to use it provides peace of mind when you catch errors immediately after sending. Remember that prevention through careful review before sending remains the most reliable strategy. Always take a moment to verify recipient addresses, review message content, and double-check attachments before clicking send. For critical communications, consider using Outlook’s delay send feature to create a safety window for review.
For more information on Outlook features, consult Microsoft’s official Office support documentation. If you use Outlook in a corporate environment, your IT department can provide additional guidance on recall policies and Exchange server settings specific to your organization.