How to Become an Ultrasound Technician: Easy & Essential Guide

Becoming an ultrasound technician is a rewarding healthcare career that combines technical skills with patient care. If you’re interested in how to become an ultrasound technician, you’ll need to complete specific education, certification, and licensing requirements. This comprehensive guide walks you through every step of the journey, from prerequisites to landing your first job in this growing field.
Quick Answer: To become an ultrasound technician, you’ll need to complete a 2-4 year accredited sonography program, pass the ARDMS certification exam, obtain state licensure (if required), and gain hands-on clinical experience. Most positions require at least an associate degree and professional certification to practice in hospitals, clinics, or private practices.
Tools & Materials You’ll Need
- High school diploma or GED
- Access to accredited sonography program (community college or university)
- Study materials for ARDMS (American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography) certification
- Clinical externship/internship opportunities
- Professional liability insurance
- CPR/BLS certification card
- Computer with internet access for online coursework
- Stethoscope and medical reference materials
Understanding the Ultrasound Technician Role
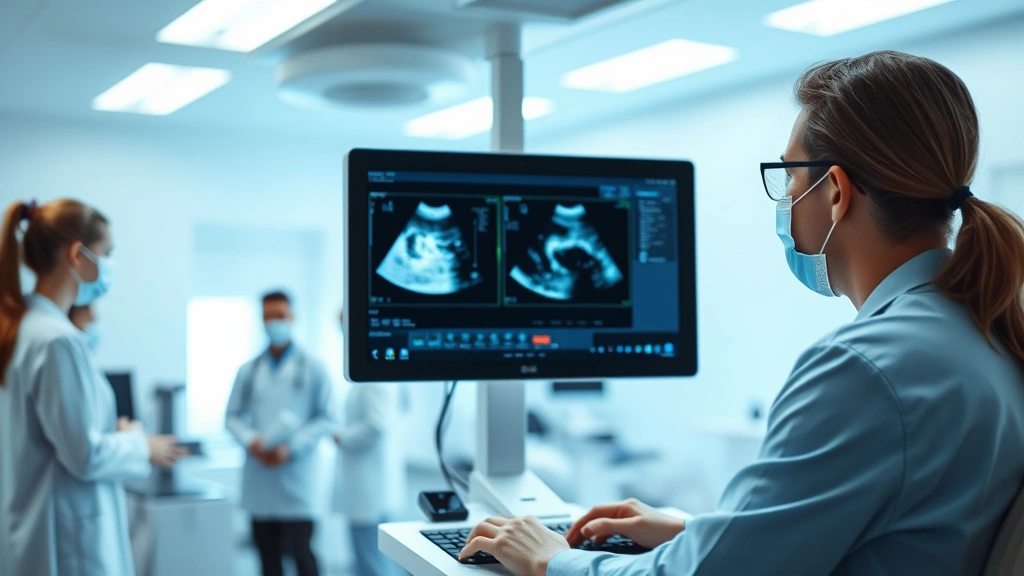
An ultrasound technician, also called a sonographer, operates specialized imaging equipment to create detailed pictures of internal organs and tissues. These professionals work directly with patients, explaining procedures and ensuring comfort during examinations. Understanding what the job entails is the first step in deciding if how to become an ultrasound technician aligns with your career goals.
Ultrasound technicians perform diagnostic imaging across various specialties including obstetrics, cardiology, abdominal imaging, and vascular sonography. You’ll be responsible for positioning patients, adjusting equipment settings, and recording images for physicians to interpret. The role requires attention to detail, compassion, and the ability to work in fast-paced healthcare environments. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, this profession is expected to grow significantly over the next decade, making it an excellent career choice for those seeking job security and advancement opportunities.
The work environment typically includes hospitals, outpatient clinics, diagnostic imaging centers, and specialty practices. Most positions require standing for extended periods and the ability to communicate clearly with diverse patient populations. This career offers excellent benefits including health insurance, retirement plans, and opportunities for continuing education.

Educational Requirements for Ultrasound Technicians
Education is fundamental when learning how to become an ultrasound technician. Most employers require at least an associate degree from an accredited sonography program. These programs typically take 2 years to complete and combine classroom instruction with hands-on clinical training. Some universities offer bachelor’s degree programs that take 4 years and provide additional depth in anatomy, physiology, and advanced imaging techniques.
Before enrolling in a sonography program, you’ll need a high school diploma or GED. Many programs also require prerequisite courses in anatomy, physiology, and basic mathematics. Some institutions offer bridge programs to help students meet these prerequisites. As reviewed by WikiHow’s educational guides, proper foundational knowledge significantly improves success in technical healthcare programs.
During your education, you’ll study ultrasound physics, instrumentation, patient care, medical ethics, and image interpretation. Coursework includes both theoretical knowledge and practical application using actual ultrasound equipment. Most programs include 40-60 hours of clinical experience where you’ll work under supervision in real healthcare settings. This hands-on training is essential for developing the technical skills and professional judgment required in the field.
Choosing the Right Sonography Program
Selecting an accredited sonography program is crucial for your success in becoming an ultrasound technician. Look for programs accredited by the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP) or the Accrediting Bureau of Health Education Schools (ABHES). Accreditation ensures the curriculum meets industry standards and that your degree will be recognized by employers nationwide.
When evaluating programs, consider factors such as program length, cost, location, and specialization options. Some programs focus on general sonography while others offer concentrations in obstetrics, cardiac, or vascular imaging. Research the program’s pass rates for the ARDMS certification exam, as this indicates the quality of instruction. Contact current students and graduates to learn about their experiences and job placement rates.
Compare tuition costs and explore financial aid options including federal student loans, grants, and scholarships. Many community colleges offer affordable 2-year programs that provide excellent preparation for certification. Universities may offer more comprehensive curricula but at higher costs. Consider your financial situation and career timeline when making this important decision. Instructables provides detailed guides on researching educational programs and making informed enrollment decisions.
Clinical Experience and Internships
Hands-on clinical experience is absolutely essential when pursuing how to become an ultrasound technician. Most accredited programs require 40-60 hours of supervised clinical work, though many students complete significantly more to build confidence and competency. Clinical externships typically occur during your final year of education and involve working in actual healthcare facilities under the supervision of experienced sonographers.
During clinical rotations, you’ll perform real ultrasound examinations on actual patients under direct supervision. This experience teaches you proper patient communication, equipment operation, and image acquisition techniques. You’ll learn to handle equipment troubleshooting, maintain patient records, and follow healthcare protocols. Many students complete internships at multiple facilities to gain exposure to different specialties and imaging equipment.
Building relationships with clinical preceptors during your internship can lead to job opportunities after graduation. Demonstrate professionalism, reliability, and enthusiasm for learning. Ask questions, seek feedback, and show initiative in your assignments. Many ultrasound technicians secure their first job through connections made during clinical training. Document your clinical hours carefully and request letters of recommendation from your preceptors to strengthen your job applications.
ARDMS Certification Exam Preparation
Passing the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS) certification exam is a critical milestone in how to become an ultrasound technician. Most employers require certification before hiring, and many states legally mandate it for practice. The exam tests your knowledge of ultrasound physics, instrumentation, patient care, and image interpretation across your specialty area.
The ARDMS offers several certification pathways depending on your specialty. The Sonography (SPI) exam covers general sonography principles, while specialty exams focus on areas like obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), abdominal imaging, cardiac sonography, or vascular technology. You must meet specific education and clinical experience requirements before sitting for the exam. Most programs prepare you to take the exam within 6 months of graduation.
Prepare for certification by reviewing study materials provided by your program, utilizing ARDMS-approved review courses, and taking practice exams. Dedicate 2-3 months to intensive studying, focusing on weak areas identified through practice tests. Join study groups with classmates to discuss challenging concepts and stay motivated. Consumer Reports’ educational resources recommend structured study schedules and multiple review methods for technical certification exams. The exam fee is approximately $300-400, and you can typically register online through the ARDMS website.
State Licensure and Registration
State licensure requirements for ultrasound technicians vary significantly depending on where you plan to work. Some states require licensure or registration, while others have no regulatory requirements. Research your state’s specific requirements early in your education planning process. States with licensure laws typically require ARDMS certification as a prerequisite for obtaining a state license.
To check your state’s requirements, contact your state’s department of health or regulatory board for medical professionals. Some states use the term “licensure” while others use “registration” or “certification.” Understanding these distinctions is important for proper terminology and compliance. Many states reciprocally recognize certifications from other states, making it easier to relocate if needed.
Even in states without licensure requirements, obtaining ARDMS certification is strongly recommended and often required by employers. Certification demonstrates your competency and commitment to professional standards. Maintain your certification by completing continuing education credits throughout your career. Most certifications require renewal every 5 years with proof of continuing education hours.
Finding Your First Job as an Ultrasound Technician
Landing your first position as an ultrasound technician requires strategic job searching and professional networking. Start by leveraging connections from your clinical internships, as many facilities hire students they’ve trained. Check job boards on hospital websites, healthcare recruitment sites like Indeed and LinkedIn, and professional organizations like the Society of Diagnostic Medical Sonography (SDMS).
Prepare a strong resume highlighting your education, ARDMS certification, clinical experience, and any specialized training. Include specific details about the types of ultrasound examinations you’ve performed and equipment you’re proficient with. Write a compelling cover letter that demonstrates your passion for patient care and commitment to professional excellence. The Spruce offers professional resume and cover letter guidance applicable to healthcare positions.
During interviews, emphasize your clinical experience, certification status, and ability to work effectively in team environments. Be prepared to discuss challenging cases you encountered during training and how you handled them. Ask thoughtful questions about the facility’s equipment, training opportunities, and patient population. Many healthcare facilities offer sign-on bonuses, tuition reimbursement, or loan forgiveness programs for new graduates. Negotiate these benefits when possible, as they can significantly impact your financial situation.
Career Advancement and Specializations
After establishing yourself as an ultrasound technician, numerous advancement opportunities exist. Many technicians pursue additional certifications in specialized areas such as cardiac sonography, vascular technology, or breast sonography. These specializations often lead to higher salaries and more interesting work. Some technicians advance into supervisory or management roles, overseeing departments and training new staff.
Consider pursuing a bachelor’s degree or master’s degree in sonography or a related healthcare field. Advanced education opens doors to teaching positions, research opportunities, or specialized clinical roles. Some ultrasound technicians transition into sales and support roles for ultrasound equipment manufacturers, combining their technical knowledge with business skills. Professional memberships in organizations like the SDMS provide networking opportunities and access to continuing education.
Stay current with technological advances in ultrasound imaging by attending conferences and completing continuing education. The field constantly evolves with new equipment, techniques, and applications. Demonstrating commitment to professional development makes you a valuable employee and increases your earning potential. Many experienced technicians earn $70,000-$90,000 annually, with supervisory positions commanding even higher salaries.
FAQ
How long does it take to become an ultrasound technician?
Most programs take 2-4 years to complete, depending on whether you pursue an associate or bachelor’s degree. Add 2-3 months for certification exam preparation and study. From start to first job typically takes 2.5-4.5 years.
What is the average salary for ultrasound technicians?
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salary is approximately $63,000-$75,000, with experienced technicians and those in specialized areas earning significantly more. Salaries vary by location, facility type, and specialization.
Do I need to be certified to work as an ultrasound technician?
While requirements vary by state, most employers require ARDMS certification. Some states legally mandate certification for practice. Even in states without requirements, certification is strongly recommended and improves job prospects.
What specializations are available for ultrasound technicians?
Common specializations include obstetrics and gynecology, cardiac sonography, abdominal imaging, vascular technology, breast sonography, and musculoskeletal ultrasound. Each specialty requires additional training and certification.
Is there high demand for ultrasound technicians?
Yes, the Bureau of Labor Statistics projects strong growth in this field due to an aging population and increased use of diagnostic imaging. Healthcare facilities consistently report difficulty finding qualified ultrasound technicians, making it an excellent career choice.
Can I work as an ultrasound technician without a degree?
Most employers require at least an associate degree from an accredited program. Some states legally require formal education for licensure. Without formal education, you cannot become a registered ultrasound technician.
What personal qualities make a good ultrasound technician?
Success in this field requires strong communication skills, attention to detail, patience with patients, physical stamina, technical aptitude, and commitment to continuing education. Compassion and professionalism are equally important as technical skills.
Learning how to become an ultrasound technician involves dedication to education, clinical training, and professional certification. The journey requires commitment but leads to a fulfilling healthcare career with excellent job security and advancement opportunities. Start by researching accredited programs in your area and taking the first step toward this rewarding profession. Family Handyman’s career planning resources and HowStuffWorks’ professional development guides offer additional insights into career planning and skill development. Your future in ultrasound technology awaits—begin your journey today!