How to Encrypt Email in Outlook: Essential & Easy Steps

Email security is no longer optional—it’s essential. If you handle sensitive information, financial details, or confidential business communications, learning how to encrypt email in Outlook is a critical skill. Outlook offers multiple encryption methods that protect your messages from unauthorized access, ensuring only intended recipients can read your content. This guide walks you through every method, from basic built-in encryption to advanced security protocols, so you can safeguard your communications today.
Quick Answer
To encrypt email in Outlook, use the Encrypt button in the ribbon (Outlook 2016+), apply Office 365 Message Encryption for cloud-based accounts, or enable S/MIME encryption for advanced security. Desktop users can access encryption via the Options menu, while web users rely on built-in Microsoft encryption features. Each method requires different setup steps but all provide end-to-end protection for sensitive messages.
Tools & Materials Needed
- Microsoft Outlook (2016 or newer, or Outlook on the Web)
- Microsoft 365 subscription (for Office 365 Message Encryption)
- Digital certificate (for S/MIME encryption)
- Recipient email address
- Internet connection
- Administrative access (for organizational encryption policies)
Understanding Email Encryption in Outlook
Email encryption scrambles your message content using mathematical algorithms, making it unreadable to anyone except authorized recipients. When you learn how to encrypt email in Outlook, you’re essentially adding a digital lock to your messages. Without the correct decryption key, intercepted emails remain gibberish—even if hackers access them during transmission or storage.
Outlook supports three primary encryption methods: the built-in Encrypt button (simplest for most users), Office 365 Message Encryption (cloud-based, enterprise-friendly), and S/MIME (industry-standard, certificate-based). Each offers different security levels and compatibility options. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right method for your specific needs, whether you’re protecting personal financial information or corporate trade secrets.
According to WikiHow, email encryption has become standard practice for professionals handling sensitive data. The choice between methods depends on your Outlook version, organizational requirements, and whether recipients use Outlook or other email clients.

How to Encrypt Email Using the Encrypt Button
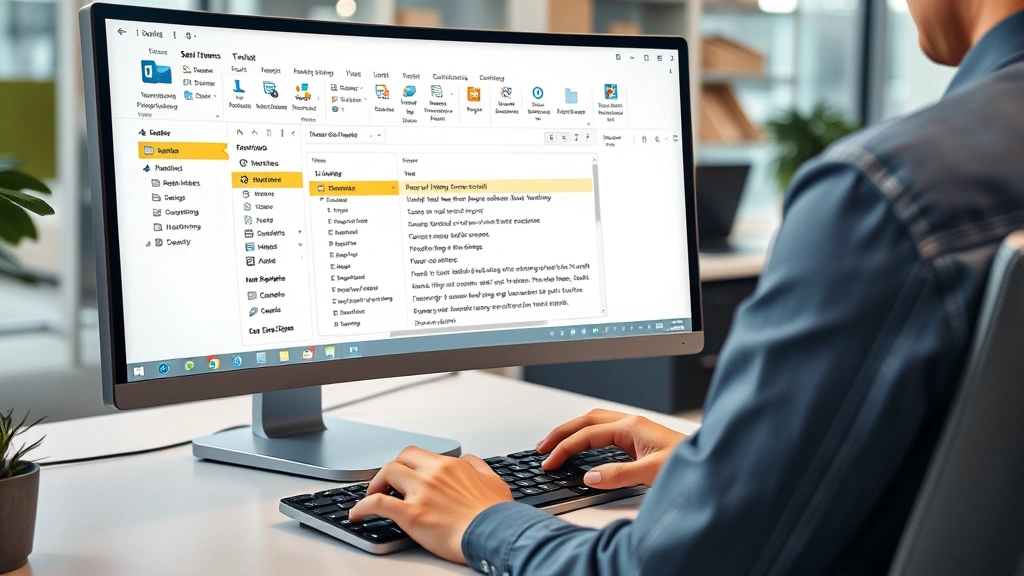
The simplest way how to encrypt email in Outlook is using the dedicated Encrypt button, available in Outlook 2016 and later versions. This method requires no certificate setup and works seamlessly with recipients using any email client. Start by composing a new email message as usual, then locate the Encrypt button in the ribbon’s Options tab.
Step-by-step process:
- Open Outlook and click New Email to create a message
- Navigate to the Options tab in the ribbon
- Click the Encrypt button (it resembles a padlock icon)
- Select your preferred encryption level from the dropdown menu
- Enter recipient email address and compose your message
- Click Send to dispatch the encrypted message
When recipients receive your encrypted email, they’ll see a secure message link. They can open it directly in Outlook or through a web browser, even if they don’t have Office 365. Microsoft handles the encryption backend automatically, so you don’t need to manage certificates or complex configurations. This method is ideal for occasional sensitive communications.
For users concerned about email security, this approach balances protection with simplicity. As reviewed by Consumer Reports, built-in encryption features reduce security risks for average users significantly.
Setting Up Office 365 Message Encryption
Office 365 Message Encryption is the enterprise-grade solution for how to encrypt email in Outlook when using cloud-based Microsoft accounts. This method provides automatic encryption for all outgoing messages to external recipients and allows administrators to create custom branding and expiration policies. Organizations can enforce encryption organization-wide, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
For administrators setting up encryption:
- Log into the Microsoft 365 admin center with administrator credentials
- Navigate to Settings > Org settings > Security & Privacy
- Select Office 365 Message Encryption
- Click Manage and enable encryption rules
- Configure transport rules to encrypt messages automatically
- Customize branding, expiration dates, and recipient permissions
- Save and apply settings organization-wide
Once enabled, users can encrypt individual messages or administrators can apply automatic encryption based on recipient domain, sender, or message classification. Recipients receive encrypted messages through a secure portal, maintaining your organization’s branding and security standards. This system is particularly valuable for healthcare, legal, and financial organizations handling regulated information.
The advantage of Office 365 encryption is centralized management and audit trails. Administrators track who accessed encrypted messages, when they were opened, and whether they were forwarded—critical for compliance documentation. Unlike basic encryption, this solution provides granular control over message lifecycles.
Enabling S/MIME Encryption for Desktop Outlook
S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) is the industry-standard encryption protocol trusted by security professionals worldwide. When you learn how to encrypt email in Outlook using S/MIME, you gain the most robust protection available. However, this method requires obtaining a digital certificate—a unique digital credential that identifies you and enables encryption.
Obtaining a digital certificate:
- Purchase from trusted Certificate Authorities (VeriSign, Comodo, Sectigo)
- Request from your organization’s IT department
- Obtain free certificates from some providers for personal use
- Cost ranges from free to $150+ annually depending on certificate type
Installing your certificate in Outlook:
- Open Outlook and go to File > Options > Trust Center
- Click Trust Center Settings
- Select Email Security from the left sidebar
- Click Import/Export to import your certificate file
- Select your certificate file (typically .pfx or .p7b format)
- Enter your certificate password when prompted
- Click OK to complete installation
Sending S/MIME encrypted messages:
- Compose a new email in Outlook
- Click Options > More Options (or similar, depending on version)
- Check Encrypt message contents and attachments
- Ensure Add digital signature is also enabled
- Add recipient and compose your message
- Click Send
S/MIME encryption requires recipients to have your public certificate to decrypt messages. When you send an S/MIME encrypted email, Outlook automatically includes your certificate, allowing recipients to reply with encrypted messages. This method provides the strongest security available and works across different email platforms, making it ideal for cross-organizational communication.
As explained by Family Handyman‘s security section, S/MIME represents the gold standard for professional email security. The process requires more setup but provides unmatched protection for highly sensitive information.
Encrypting Email in Outlook on the Web
Outlook on the Web (formerly Outlook.com) users can also encrypt messages, though the process differs slightly from desktop versions. This method works for anyone accessing Outlook through a web browser, making it accessible whether you’re at your office, home, or traveling.
How to encrypt email in Outlook on the Web:
- Sign into Outlook.com or Outlook.office.com
- Click New Message to start composing
- Click the three dots (More options) button
- Select Encrypt from the dropdown menu
- Choose your encryption settings from available options
- Enter recipient email address and message content
- Click Send to deliver the encrypted message
Web-based encryption in Outlook uses the same Office 365 Message Encryption backend as desktop versions. Recipients receive a secure link and can open the message through their browser without installing additional software. This approach is perfect for users who primarily work through mobile devices or web browsers.
One advantage of web encryption is automatic cloud backup. Your encrypted messages are stored securely in Microsoft’s data centers with redundant backups, protecting against device loss or failure. Recipients can access encrypted messages indefinitely through the secure portal, even if they delete the original email.
Troubleshooting Common Encryption Issues
Even when you understand how to encrypt email in Outlook, technical issues occasionally arise. Common problems include encryption buttons appearing grayed out, recipients unable to open encrypted messages, or certificate installation failures. Most issues have straightforward solutions.
Encrypt button is grayed out or missing:
- Verify you’re using Outlook 2016 or newer version
- Check that Microsoft 365 or Office 365 subscription is active
- Restart Outlook completely and try again
- Update Outlook to the latest version through Windows Update
- Ensure you’re composing an email (not a meeting or task)
Recipients cannot open encrypted messages:
- Confirm recipient email address is correct and active
- For S/MIME, verify recipient has your public certificate
- Check recipient’s spam folder for secure message notification
- Ask recipient to try opening message in different browser
- Confirm recipient’s email provider supports encrypted messages
Certificate installation fails:
- Verify certificate file format (.pfx, .p7b, or .cer)
- Ensure you have the correct certificate password
- Try importing certificate with administrator privileges
- Contact certificate provider if file is corrupted or expired
- Check that your Windows user account has permission to install certificates
If problems persist, contact Microsoft Support or your organization’s IT department. They can verify your account settings, check encryption policies, and provide version-specific guidance. According to HowStuffWorks, most encryption issues resolve through simple troubleshooting steps.
Best Practices for Secure Email Communication
Knowing how to encrypt email in Outlook is just the first step toward secure communication. Implementing best practices ensures your encryption remains effective and protects against other security vulnerabilities.
Essential security practices:
- Encrypt sensitive information consistently: Make encryption your default for any message containing personal, financial, or confidential data
- Use strong passwords: Protect your Outlook account with complex, unique passwords updated regularly
- Enable two-factor authentication: Add an extra security layer to prevent unauthorized account access
- Verify recipient addresses: Double-check email addresses before sending encrypted messages to prevent misdirection
- Update software regularly: Keep Outlook and Windows updated with latest security patches
- Be cautious with attachments: Encrypt emails containing sensitive file attachments with the same rigor as text content
- Educate recipients: Ensure recipients understand how to open and handle encrypted messages securely
- Monitor access logs: For Office 365 encryption, regularly review who accessed encrypted messages and when
Additionally, consider your organization’s compliance requirements. Healthcare organizations must follow HIPAA regulations, financial institutions must adhere to SEC rules, and legal firms must protect attorney-client privilege. Encryption helps meet these requirements, but it’s one component of comprehensive security strategy. As reviewed by The Spruce‘s digital security guides, layered security approaches provide maximum protection.
You should also educate colleagues about how to recall an email in Outlook and how to retract an email in Outlook, which provide additional safety nets if you accidentally send unencrypted messages. These complementary features add extra layers of protection for your communications.
For users managing multiple email accounts, consider how to set out of office in Outlook to inform senders when you’re unavailable. This prevents sensitive messages from sitting unread during your absence. While not directly related to encryption, proper out-of-office messages reduce security risks by setting appropriate expectations.
FAQ
Can I encrypt emails to non-Outlook users?
Yes, absolutely. When you use the Encrypt button or Office 365 Message Encryption, recipients receive a secure link they can open through any web browser. S/MIME encryption works with any email client that supports S/MIME protocol. Recipients don’t need Outlook installed to read your encrypted messages.
Does encryption slow down email delivery?
No. Encryption happens almost instantaneously before sending. Your message reaches recipients at normal speed. The encryption process adds negligible delay—typically milliseconds—that users never notice. Cloud-based encryption may actually improve speed by leveraging Microsoft’s optimized servers.
What’s the difference between encryption and digital signatures?
Encryption scrambles your message so only intended recipients can read it. Digital signatures verify that you sent the message and confirm it hasn’t been altered. You can use either independently, but combining both provides maximum security: encryption protects content while signatures prove authenticity.
Can I encrypt emails automatically?
Yes. Administrators can set up transport rules in Office 365 to automatically encrypt messages based on criteria like recipient domain, sender, or content keywords. Desktop Outlook doesn’t offer automatic encryption, but you can enable S/MIME as your default signing and encryption method for all messages.
Is encrypted email compliant with regulations?
Encryption helps meet compliance requirements for HIPAA, GDPR, PCI-DSS, and other regulations. However, encryption alone doesn’t guarantee compliance. You must implement comprehensive security policies including access controls, audit logging, and data retention procedures. Consult with your compliance officer about specific requirements.
What happens if I lose my encryption certificate?
If you lose your S/MIME certificate, you cannot decrypt previously encrypted emails sent to you. Always maintain secure backups of your certificates. Your Certificate Authority may provide recovery options, but some certificates cannot be recovered. For critical communications, keep unencrypted backups or use Office 365 encryption instead.
Can recipients forward encrypted emails?
This depends on your encryption method and settings. Office 365 Message Encryption allows administrators to restrict forwarding. S/MIME encryption can’t technically prevent forwarding, but recipients understand they’re receiving confidential information. For maximum security, use Office 365 encryption with forwarding restrictions enabled.
Does encryption work with Outlook mobile apps?
Yes. Outlook mobile apps support Office 365 Message Encryption. Users can open encrypted messages through the secure web portal. However, S/MIME support on mobile varies by app and device. For mobile users, Office 365 encryption provides the most reliable cross-platform experience.